Pedodontics Treatments
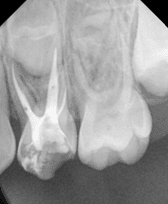
Pulpectomy/ Pulpotomy Procedures
Pulpectomy is an endodontic procedure indicated indicated for the treatment of pulp necrosis or non vital primary teeth. It involves the complete extirpation of both the coronal as well as the radicular pulp unlike pulpotomy where only the coronal pulp is removed. It is considered as a conservative treatment approach to prevent premature loss of a tooth and subsequent loss of arch length. The procedure involves the deroofing of the pulp chamber to gain access to the canal orifices followed by instrumentation for debridement, enlargement and disinfection of the root canals . This is followed by the filling with various obturating materials which are biocompatible and ideally resorbable. Obturating materials used in primary teeth after pulpectomy include zinc oxide eugenol, calcium hydroxide with iodoform paste, calcium hydroxide with CPC, KRI paste.
In addition, pulpectomy is also advantageous for retained primary molar teeth. If not severed with a progressive root resorption or aligned in a severe infra-occlusion, the retained molar can be a functional component in the dental arch.
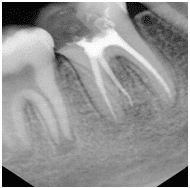
Root Canal Treatment
The root canal treatment procedure, also known as endodontic treatment, is a common procedure in modern dentistry that is used to remove inflamed or infected tissue from inside a tooth.When a tooth's nerve tissue or pulp is damaged, it breaks down and bacteria begin to multiply within the pulp chamber. The bacteria and other decayed debris can cause an infection or abscessed tooth. patient will experience Severe pain upon chewing or application of pressure, Prolonged sensitivity (pain) to hot or cold temperatures (after the heat or cold has been removed),Discoloration (darkening) of the tooth and Swelling and tenderness in nearby gums. Root Canal Procedure. If root canal treatment is not carried out swelling may spread to other areas of the face, neck, or head, there would be Bone Loss around the tip of the root. Drainage of pus will be seen extending outward from the root. A hole can occur through the side of the tooth with drainage into the gums or through the cheek with drainage into the skin.
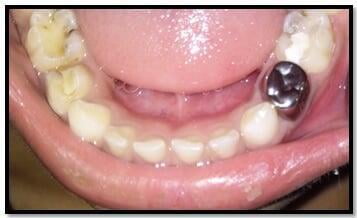
Stainless Steel Crowns
The stainless-steel crown (SSC) is an extremely durable restoration with several clear-cut indications for use in primary teeth including: following a pulpotomy/pulpectomy; for teeth with developmental defects or large carious lesions involving multiple surfaces where an amalgam is likely to fail; and for fractured teeth. In other situations, its use is less clear cut, and caries risk factors, restoration longevity and cost effectiveness are considerations in decisions to use the SSC.caries risk factors in young children indicates that children at high risk exhibiting anterior tooth decay and/or molar caries may benefit by treatment with stainless steel crowns to protect the remaining at-risk tooth surfaces. Studies evaluating restoration longevity, including the durability and lifespan of SSCs and Class II amalgams demonstrate the superiority of SSCs for both parameters. Children with extensive decay, large lesions or multiple surface lesions in primary molars should be treated with stainless steel crowns. Because of the protection from future decay provided by their feature of full coverage and their increased durability and longevity, strong consideration is to be given to the use of SSCs .
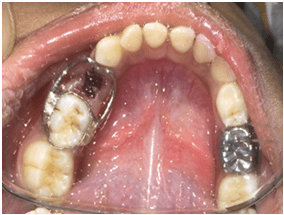
Composite Restoration
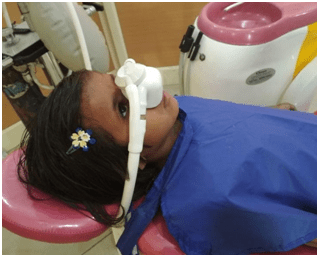
Conscious Sedation
Dental procedures are a common source of fear, pain and anxiety in children due to which it becomes difficult to deliver appropriate treatment in pediatric patients. So it is the duty of every Pedodontist, to recognize the behavior that produces anxiety in a child during dental treatment and to use various behavior management strategies to overcome it. Majority of the pediatric patients can be managed by routine non- pharmacological behaviour management techniques; however, some children exhibit very negative behaviour in dental clinic and refuse to undergo any kind of dental treatment. In such cases, pharmacological behaviour management plays its role in reducing fear and anxiety, thereby making the child calm and relaxed during the dental procedure. One such modality is Nitrous oxide- Oxygen inhalation sedationwhich is the safest and the most frequently used technique for the management of fear and anxiety in children.
Nitrous oxide-oxygen sedation reduces anxiety, produces adequate sedation and enhances communication and patient cooperation; with vital signs within normal limits and treatments successfully completed.
